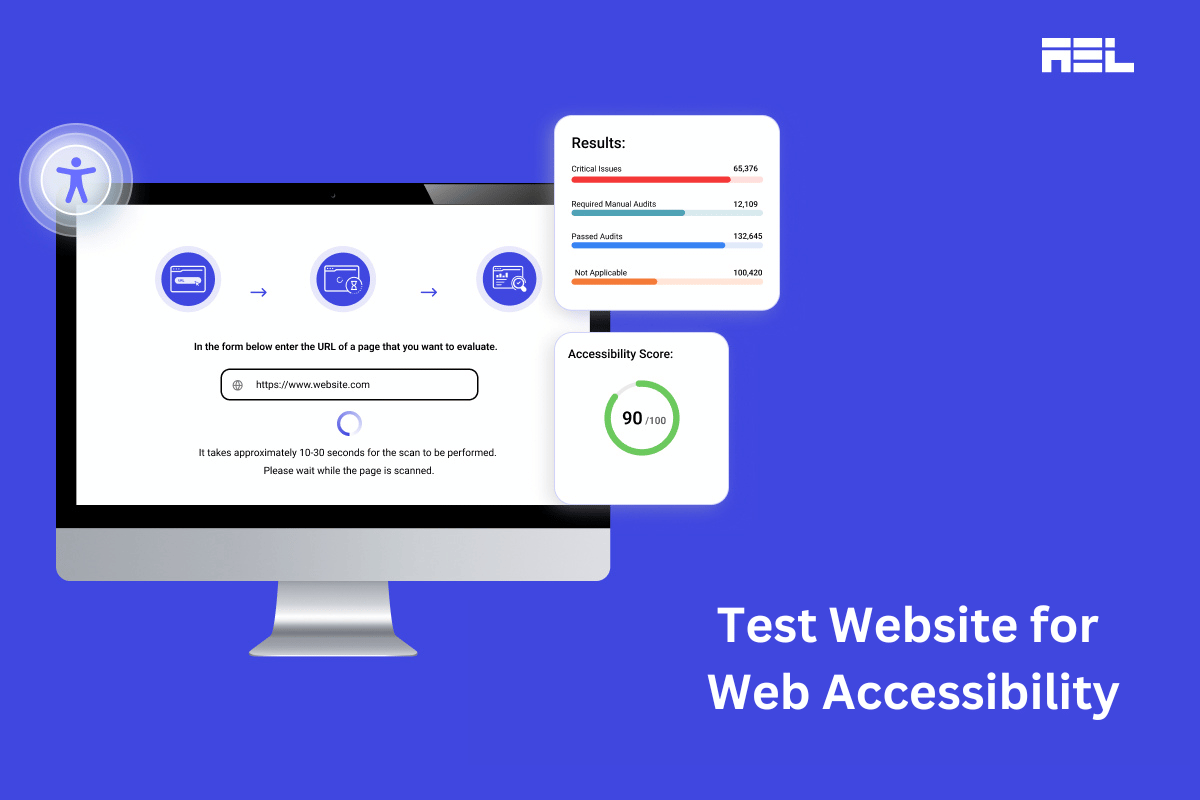
In the current digital world, ensuring that your website is accessible to your users has become more vital than ever. In the following FAQs, we will address some crucial questions and help you understand the process of testing a website for accessibility even better.
You could be a beginner who just got introduced to the topic of accessibility testing or could be an expert looking to enhance your current practices.
Table of Contents
Steps to follow to improve the accessibility of your website
Either way, the below answers will help you improve the accessibility of your website.
1. Validate your website’s code
To ensure your website meets high standards, try an HTML Validator. This tool checks your code to meet World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) standards, making it error-free and improving your website’s quality, speed, and user-friendliness.
Unchecked HTML usually contains errors that pop up when your site goes live, causing pages to break, browsers to act up, and users to struggle to access your content. Validating your HTML against W3C standards ensures it functions smoothly.
W3C compatibility guarantees your HTML is in good shape. To validate your code, turn to W3C’s validation tools like the HTML and CSS validators. Browser extensions also exist to check your pages against W3C standards.
2. Alt text, captions, transcripts and color contrast
Describing images, adding captions to multimedia, providing transcripts, and adjusting color contrast are essential for accessibility. Ensure images have detailed alt text, and multimedia content such as videos and podcasts include accurate captions or transcripts.
Test video players with accessibility features enabled. Verify text and background color contrast using tools like WebAIM’s Color Contrast Checker. Meet WCAG requirements for contrast ratios.
3. Check for keyboard accessibility
Ensure all interactive elements on your website can be accessed and used with a keyboard alone. Test tab order and focus indicators to ensure smooth navigation. Logical tab order helps keyboard-only users navigate easily. Clean, semantic code ensures proper tab order without the need for explicit scripting.
4. Test with assistive technology
Assistive technologies like screen readers, magnifiers, text-to-speech, and speech input assist people with disabilities in accessing digital content. These tools connect the gap for users with various impairments, providing equal access to information and functionality.
From visually impaired users to those with mobility issues, assistive technologies cater to diverse needs, ensuring accessibility in digital environments.
5. Compliance to WCAG
Ensure your website complies with WCAG 2.1 Level AA success criteria. Use WCAG checklist tools to review accessibility criteria systematically.
6. User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
Conduct User Acceptance Testing (UAT) with individuals having different disabilities. Invite users with disabilities to test your website and gather feedback to identify web accessibility issues not caught by automated testing. Insights from diverse users help understand real-world accessibility challenges.
7. Feedback loop
Incorporate ongoing accessibility checks into your development and testing routines. Regular accessibility testing ensures early issue detection and continuous improvement. Make accessibility testing a standard practice in your development process.
Wrapping Up
Are you curious to explore how AEL Data’s web accessibility checker can streamline your website’s accessibility testing process? Visit AAC to learn more about our innovative tool and ensure your website is accessible to all users!